Jak stworzyć własny token ERC-721? [Ethereum]
Tokeny ERC-721 reprezentują unikatową wartość zasobu lub towaru w postaci smart contractu na blockchainie (najczęściej na platformie Ethereum). Główną cechą tokenu ERC-721 jest wartość indywidualna każdej sztuki. Na przykład bilet lotniczy – w samolocie każdy posiada taki sam – lecz są one wydawane personalnie, dzieło sztuki namalowane przez artystę – każdy obraz może mieć inną wartość, lub gry kolekcjonerskie – każda karta może znaczyć coś innego.
Najbardziej kojarzone są z grą Crypto Kitties. Tokeny ERC-721 często nazywane również NFT (ang. non-fungible tokens) – co dosłownie oznacza, że są “niewymienialne”. Podczas gdy większość tokenów jest zamienna (token jest taki sam jak każdy inny), wszystkie tokeny ERC-721 są unikalne. Innymi słowy każdy token NFT jest unikalny w stosunku do pozostałych tokenów w danym łańcuchu.
Tworzymy token ERC-721 krok po kroku
Token będziemy tworzyć na maszynie wirtualnej Ethereum (w skrócie EVM – Ethereum Virtual Machine). Możemy wybrać z trzech najpopularniejszych:
Zintegrowane środowiska programistyczne (w skrócie IDE) różnią się interfejsem i niekiedy funkcjonalnością – w niektórych trzeba dany plugin samemu napisać w formie kodu. Każdy program działający na EVM jest powszechnie nazywany „inteligentnym kontraktem” (ang. „smart contract”). Najpopularniejsze języki, w których tworzy się inteligentne kontrakty w Ethereum to Solidity i Vyper, ale istnieją także inne, będące w fazie rozwoju. Nasz pierwszy token będziemy tworzyć na platformie Remix.
Sprawdź również nasz poradnik dotyczący tworzenia tokenów ERC-20.
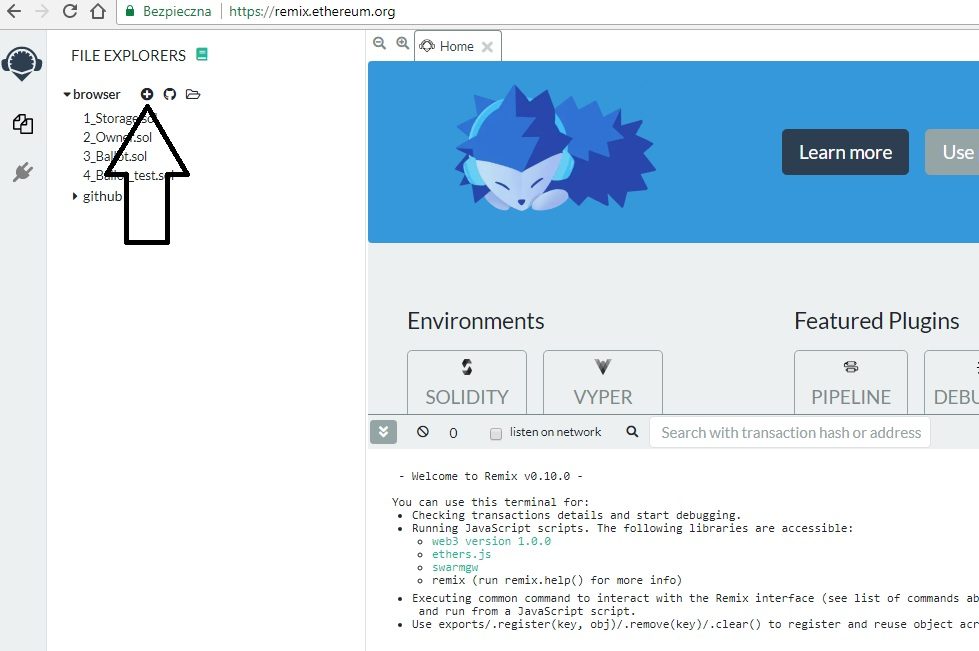
1) Wchodzimy na stronę – https://remix.ethereum.org i klikamy “+”, aby stworzyć nowy kontrakt/program na blockchainie:
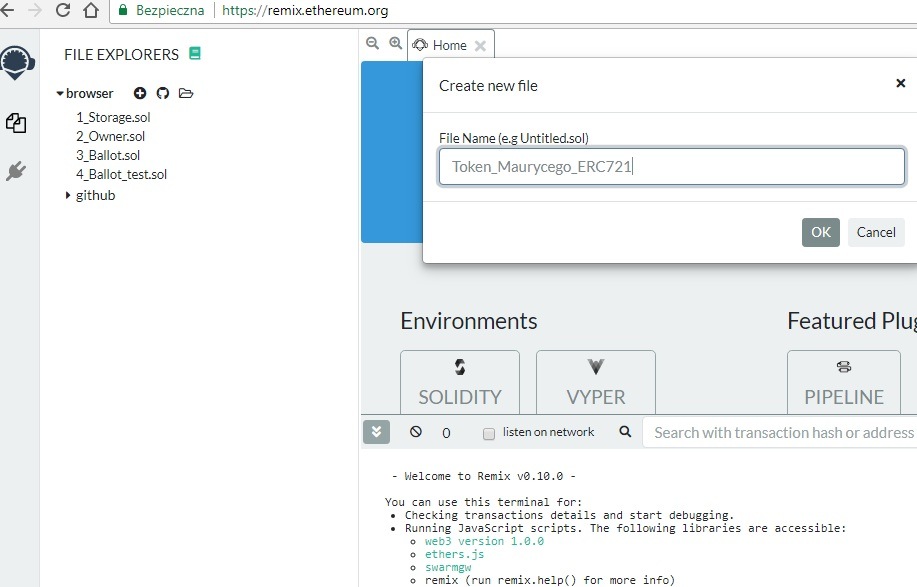
2) Nazywamy nasz projekt, żeby nie pomylić go w przyszłości: i klikamy “+”, aby stworzyć nowy smart contract (program na blockchainie):
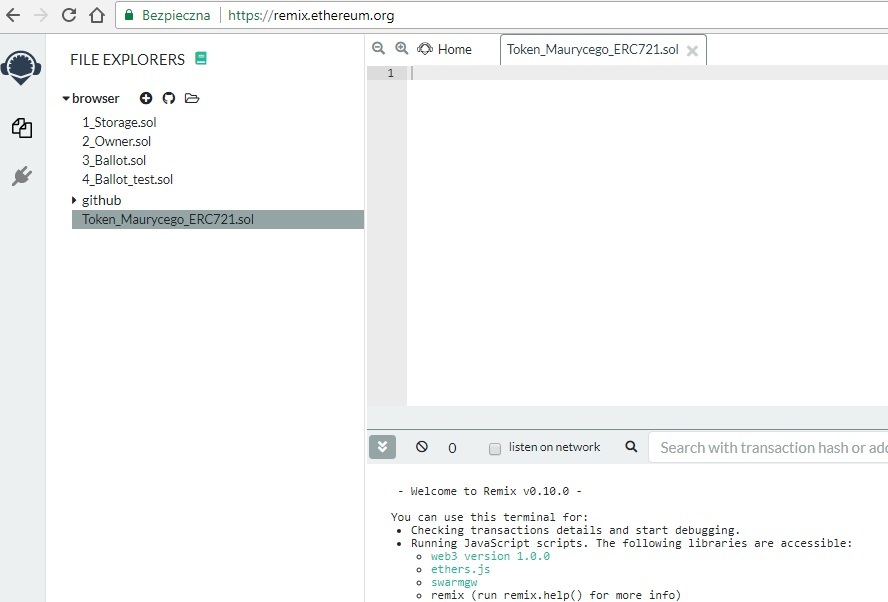
3) Zatwierdzamy “OK” i przechodzimy do pisania naszego smart contractu, który będzie tokenem:
4) Wklejamy następujący kod (w całości) smart contractu, który odpowiada za tworzenie tokenu (pogrubiony tekst nie jest konieczny – opisuje funkcjonowanie). Pełną dokumentację kodu można znaleźć na https://github.com/nibbstack/erc721:
pragma solidity 0.6.2;
// ERC Token Standard #721
// All documentation is available on the website:
// https://github.com/0xceart/ethereum-erc721
/**
* @dev ERC-721 non-fungible token standard.
* See https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-721.md.
*/
interface ERC721
{
/**
* @dev Emits when ownership of any NFT changes by any mechanism. This event emits when NFTs are
* created (`from` == 0) and destroyed (`to` == 0). Exception: during contract creation, any
* number of NFTs may be created and assigned without emitting Transfer. At the time of any
* transfer, the approved address for that NFT (if any) is reset to none.
*/
event Transfer(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/**
* @dev This emits when the approved address for an NFT is changed or reaffirmed. The zero
* address indicates there is no approved address. When a Transfer event emits, this also
* indicates that the approved address for that NFT (if any) is reset to none.
*/
event Approval(
address indexed _owner,
address indexed _approved,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/**
* @dev This emits when an operator is enabled or disabled for an owner. The operator can manage
* all NFTs of the owner.
*/
event ApprovalForAll(
address indexed _owner,
address indexed _operator,
bool _approved
);
/**
* @dev Transfers the ownership of an NFT from one address to another address.
* @notice Throws unless `msg.sender` is the current owner, an authorized operator, or the
* approved address for this NFT. Throws if `_from` is not the current owner. Throws if `_to` is
* the zero address. Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT. When transfer is complete, this
* function checks if `_to` is a smart contract (code size > 0). If so, it calls
* `onERC721Received` on `_to` and throws if the return value is not
* `bytes4(keccak256("onERC721Received(address,uint256,bytes)"))`.
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
* @param _data Additional data with no specified format, sent in call to `_to`.
*/
function safeTransferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
bytes calldata _data
)
external;
/**
* @dev Transfers the ownership of an NFT from one address to another address.
* @notice This works identically to the other function with an extra data parameter, except this
* function just sets data to ""
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
*/
function safeTransferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external;
/**
* @dev Throws unless `msg.sender` is the current owner, an authorized operator, or the approved
* address for this NFT. Throws if `_from` is not the current owner. Throws if `_to` is the zero
* address. Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT.
* @notice The caller is responsible to confirm that `_to` is capable of receiving NFTs or else
* they mayb be permanently lost.
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
*/
function transferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external;
/**
* @dev Set or reaffirm the approved address for an NFT.
* @notice The zero address indicates there is no approved address. Throws unless `msg.sender` is
* the current NFT owner, or an authorized operator of the current owner.
* @param _approved The new approved NFT controller.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to approve.
*/
function approve(
address _approved,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external;
/**
* @dev Enables or disables approval for a third party ("operator") to manage all of
* `msg.sender`'s assets. It also emits the ApprovalForAll event.
* @notice The contract MUST allow multiple operators per owner.
* @param _operator Address to add to the set of authorized operators.
* @param _approved True if the operators is approved, false to revoke approval.
*/
function setApprovalForAll(
address _operator,
bool _approved
)
external;
/**
* @dev Returns the number of NFTs owned by `_owner`. NFTs assigned to the zero address are
* considered invalid, and this function throws for queries about the zero address.
* @param _owner Address for whom to query the balance.
* @return Balance of _owner.
*/
function balanceOf(
address _owner
)
external
view
returns (uint256);
/**
* @dev Returns the address of the owner of the NFT. NFTs assigned to zero address are considered
* invalid, and queries about them do throw.
* @param _tokenId The identifier for an NFT.
* @return Address of _tokenId owner.
*/
function ownerOf(
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
view
returns (address);
/**
* @dev Get the approved address for a single NFT.
* @notice Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to find the approved address for.
* @return Address that _tokenId is approved for.
*/
function getApproved(
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
view
returns (address);
/**
* @dev Returns true if `_operator` is an approved operator for `_owner`, false otherwise.
* @param _owner The address that owns the NFTs.
* @param _operator The address that acts on behalf of the owner.
* @return True if approved for all, false otherwise.
*/
function isApprovedForAll(
address _owner,
address _operator
)
external
view
returns (bool);
}
/**
* @dev ERC-721 interface for accepting safe transfers.
* See https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-721.md.
*/
interface ERC721TokenReceiver
{
/**
* @dev Handle the receipt of a NFT. The ERC721 smart contract calls this function on the
* recipient after a `transfer`. This function MAY throw to revert and reject the transfer. Return
* of other than the magic value MUST result in the transaction being reverted.
* Returns `bytes4(keccak256("onERC721Received(address,address,uint256,bytes)"))` unless throwing.
* @notice The contract address is always the message sender. A wallet/broker/auction application
* MUST implement the wallet interface if it will accept safe transfers.
* @param _operator The address which called `safeTransferFrom` function.
* @param _from The address which previously owned the token.
* @param _tokenId The NFT identifier which is being transferred.
* @param _data Additional data with no specified format.
* @return Returns `bytes4(keccak256("onERC721Received(address,address,uint256,bytes)"))`.
*/
function onERC721Received(
address _operator,
address _from,
uint256 _tokenId,
bytes calldata _data
)
external
returns(bytes4);
}
/**
* @dev Math operations with safety checks that throw on error. This contract is based on the
* source code at:
* https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-solidity/blob/master/contracts/math/SafeMath.sol.
*/
library SafeMath
{
/**
* List of revert message codes. Implementing dApp should handle showing the correct message.
* Based on 0xcert framework error codes.
*/
string constant OVERFLOW = "008001";
string constant SUBTRAHEND_GREATER_THEN_MINUEND = "008002";
string constant DIVISION_BY_ZERO = "008003";
/**
* @dev Multiplies two numbers, reverts on overflow.
* @param _factor1 Factor number.
* @param _factor2 Factor number.
* @return product The product of the two factors.
*/
function mul(
uint256 _factor1,
uint256 _factor2
)
internal
pure
returns (uint256 product)
{
// Gas optimization: this is cheaper than requiring 'a' not being zero, but the
// benefit is lost if 'b' is also tested.
// See: https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-solidity/pull/522
if (_factor1 == 0)
{
return 0;
}
product = _factor1 * _factor2;
require(product / _factor1 == _factor2, OVERFLOW);
}
/**
* @dev Integer division of two numbers, truncating the quotient, reverts on division by zero.
* @param _dividend Dividend number.
* @param _divisor Divisor number.
* @return quotient The quotient.
*/
function div(
uint256 _dividend,
uint256 _divisor
)
internal
pure
returns (uint256 quotient)
{
// Solidity automatically asserts when dividing by 0, using all gas.
require(_divisor > 0, DIVISION_BY_ZERO);
quotient = _dividend / _divisor;
// assert(_dividend == _divisor * quotient + _dividend % _divisor); // There is no case in which this doesn't hold.
}
/**
* @dev Substracts two numbers, throws on overflow (i.e. if subtrahend is greater than minuend).
* @param _minuend Minuend number.
* @param _subtrahend Subtrahend number.
* @return difference Difference.
*/
function sub(
uint256 _minuend,
uint256 _subtrahend
)
internal
pure
returns (uint256 difference)
{
require(_subtrahend <= _minuend, SUBTRAHEND_GREATER_THEN_MINUEND);
difference = _minuend - _subtrahend;
}
/**
* @dev Adds two numbers, reverts on overflow.
* @param _addend1 Number.
* @param _addend2 Number.
* @return sum Sum.
*/
function add(
uint256 _addend1,
uint256 _addend2
)
internal
pure
returns (uint256 sum)
{
sum = _addend1 + _addend2;
require(sum >= _addend1, OVERFLOW);
}
/**
* @dev Divides two numbers and returns the remainder (unsigned integer modulo), reverts when
* dividing by zero.
* @param _dividend Number.
* @param _divisor Number.
* @return remainder Remainder.
*/
function mod(
uint256 _dividend,
uint256 _divisor
)
internal
pure
returns (uint256 remainder)
{
require(_divisor != 0, DIVISION_BY_ZERO);
remainder = _dividend % _divisor;
}
}
/**
* @dev A standard for detecting smart contract interfaces.
* See: https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-165.
*/
interface ERC165
{
/**
* @dev Checks if the smart contract includes a specific interface.
* @notice This function uses less than 30,000 gas.
* @param _interfaceID The interface identifier, as specified in ERC-165.
* @return True if _interfaceID is supported, false otherwise.
*/
function supportsInterface(
bytes4 _interfaceID
)
external
view
returns (bool);
}
/**
* @dev Implementation of standard for detect smart contract interfaces.
*/
contract SupportsInterface is
ERC165
{
/**
* @dev Mapping of supported intefraces.
* @notice You must not set element 0xffffffff to true.
*/
mapping(bytes4 => bool) internal supportedInterfaces;
/**
* @dev Contract constructor.
*/
constructor()
public
{
supportedInterfaces[0x01ffc9a7] = true; // ERC165
}
/**
* @dev Function to check which interfaces are suported by this contract.
* @param _interfaceID Id of the interface.
* @return True if _interfaceID is supported, false otherwise.
*/
function supportsInterface(
bytes4 _interfaceID
)
external
override
view
returns (bool)
{
return supportedInterfaces[_interfaceID];
}
}
/**
* @dev Utility library of inline functions on addresses.
* @notice Based on:
* https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-contracts/blob/master/contracts/utils/Address.sol
* Requires EIP-1052.
*/
library AddressUtils
{
/**
* @dev Returns whether the target address is a contract.
* @param _addr Address to check.
* @return addressCheck True if _addr is a contract, false if not.
*/
function isContract(
address _addr
)
internal
view
returns (bool addressCheck)
{
// This method relies in extcodesize, which returns 0 for contracts in
// construction, since the code is only stored at the end of the
// constructor execution.
// According to EIP-1052, 0x0 is the value returned for not-yet created accounts
// and 0xc5d2460186f7233c927e7db2dcc703c0e500b653ca82273b7bfad8045d85a470 is returned
// for accounts without code, i.e. `keccak256('')`
bytes32 codehash;
bytes32 accountHash = 0xc5d2460186f7233c927e7db2dcc703c0e500b653ca82273b7bfad8045d85a470;
assembly { codehash := extcodehash(_addr) } // solhint-disable-line
addressCheck = (codehash != 0x0 && codehash != accountHash);
}
}
/**
* @dev Implementation of ERC-721 non-fungible token standard.
*/
contract NFToken is
ERC721,
SupportsInterface
{
using SafeMath for uint256;
using AddressUtils for address;
/**
* List of revert message codes. Implementing dApp should handle showing the correct message.
* Based on 0xcert framework error codes.
*/
string constant ZERO_ADDRESS = "003001";
string constant NOT_VALID_NFT = "003002";
string constant NOT_OWNER_OR_OPERATOR = "003003";
string constant NOT_OWNER_APPROWED_OR_OPERATOR = "003004";
string constant NOT_ABLE_TO_RECEIVE_NFT = "003005";
string constant NFT_ALREADY_EXISTS = "003006";
string constant NOT_OWNER = "003007";
string constant IS_OWNER = "003008";
/**
* @dev Magic value of a smart contract that can recieve NFT.
* Equal to: bytes4(keccak256("onERC721Received(address,address,uint256,bytes)")).
*/
bytes4 internal constant MAGIC_ON_ERC721_RECEIVED = 0x150b7a02;
/**
* @dev A mapping from NFT ID to the address that owns it.
*/
mapping (uint256 => address) internal idToOwner;
/**
* @dev Mapping from NFT ID to approved address.
*/
mapping (uint256 => address) internal idToApproval;
/**
* @dev Mapping from owner address to count of his tokens.
*/
mapping (address => uint256) private ownerToNFTokenCount;
/**
* @dev Mapping from owner address to mapping of operator addresses.
*/
mapping (address => mapping (address => bool)) internal ownerToOperators;
/**
* @dev Emits when ownership of any NFT changes by any mechanism. This event emits when NFTs are
* created (`from` == 0) and destroyed (`to` == 0). Exception: during contract creation, any
* number of NFTs may be created and assigned without emitting Transfer. At the time of any
* transfer, the approved address for that NFT (if any) is reset to none.
* @param _from Sender of NFT (if address is zero address it indicates token creation).
* @param _to Receiver of NFT (if address is zero address it indicates token destruction).
* @param _tokenId The NFT that got transfered.
*/
event Transfer(
address indexed _from,
address indexed _to,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/**
* @dev This emits when the approved address for an NFT is changed or reaffirmed. The zero
* address indicates there is no approved address. When a Transfer event emits, this also
* indicates that the approved address for that NFT (if any) is reset to none.
* @param _owner Owner of NFT.
* @param _approved Address that we are approving.
* @param _tokenId NFT which we are approving.
*/
event Approval(
address indexed _owner,
address indexed _approved,
uint256 indexed _tokenId
);
/**
* @dev This emits when an operator is enabled or disabled for an owner. The operator can manage
* all NFTs of the owner.
* @param _owner Owner of NFT.
* @param _operator Address to which we are setting operator rights.
* @param _approved Status of operator rights(true if operator rights are given and false if
* revoked).
*/
event ApprovalForAll(
address indexed _owner,
address indexed _operator,
bool _approved
);
/**
* @dev Guarantees that the msg.sender is an owner or operator of the given NFT.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to validate.
*/
modifier canOperate(
uint256 _tokenId
)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(tokenOwner == msg.sender || ownerToOperators[tokenOwner][msg.sender], NOT_OWNER_OR_OPERATOR);
_;
}
/**
* @dev Guarantees that the msg.sender is allowed to transfer NFT.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to transfer.
*/
modifier canTransfer(
uint256 _tokenId
)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(
tokenOwner == msg.sender
|| idToApproval[_tokenId] == msg.sender
|| ownerToOperators[tokenOwner][msg.sender],
NOT_OWNER_APPROWED_OR_OPERATOR
);
_;
}
/**
* @dev Guarantees that _tokenId is a valid Token.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to validate.
*/
modifier validNFToken(
uint256 _tokenId
)
{
require(idToOwner[_tokenId] != address(0), NOT_VALID_NFT);
_;
}
/**
* @dev Contract constructor.
*/
constructor()
public
{
supportedInterfaces[0x80ac58cd] = true; // ERC721
}
/**
* @dev Transfers the ownership of an NFT from one address to another address. This function can
* be changed to payable.
* @notice Throws unless `msg.sender` is the current owner, an authorized operator, or the
* approved address for this NFT. Throws if `_from` is not the current owner. Throws if `_to` is
* the zero address. Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT. When transfer is complete, this
* function checks if `_to` is a smart contract (code size > 0). If so, it calls
* `onERC721Received` on `_to` and throws if the return value is not
* `bytes4(keccak256("onERC721Received(address,uint256,bytes)"))`.
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
* @param _data Additional data with no specified format, sent in call to `_to`.
*/
function safeTransferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
bytes calldata _data
)
external
override
{
_safeTransferFrom(_from, _to, _tokenId, _data);
}
/**
* @dev Transfers the ownership of an NFT from one address to another address. This function can
* be changed to payable.
* @notice This works identically to the other function with an extra data parameter, except this
* function just sets data to ""
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
*/
function safeTransferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
{
_safeTransferFrom(_from, _to, _tokenId, "");
}
/**
* @dev Throws unless `msg.sender` is the current owner, an authorized operator, or the approved
* address for this NFT. Throws if `_from` is not the current owner. Throws if `_to` is the zero
* address. Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT. This function can be changed to payable.
* @notice The caller is responsible to confirm that `_to` is capable of receiving NFTs or else
* they maybe be permanently lost.
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
*/
function transferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
canTransfer(_tokenId)
validNFToken(_tokenId)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(tokenOwner == _from, NOT_OWNER);
require(_to != address(0), ZERO_ADDRESS);
_transfer(_to, _tokenId);
}
/**
* @dev Set or reaffirm the approved address for an NFT. This function can be changed to payable.
* @notice The zero address indicates there is no approved address. Throws unless `msg.sender` is
* the current NFT owner, or an authorized operator of the current owner.
* @param _approved Address to be approved for the given NFT ID.
* @param _tokenId ID of the token to be approved.
*/
function approve(
address _approved,
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
canOperate(_tokenId)
validNFToken(_tokenId)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(_approved != tokenOwner, IS_OWNER);
idToApproval[_tokenId] = _approved;
emit Approval(tokenOwner, _approved, _tokenId);
}
/**
* @dev Enables or disables approval for a third party ("operator") to manage all of
* `msg.sender`'s assets. It also emits the ApprovalForAll event.
* @notice This works even if sender doesn't own any tokens at the time.
* @param _operator Address to add to the set of authorized operators.
* @param _approved True if the operators is approved, false to revoke approval.
*/
function setApprovalForAll(
address _operator,
bool _approved
)
external
override
{
ownerToOperators[msg.sender][_operator] = _approved;
emit ApprovalForAll(msg.sender, _operator, _approved);
}
/**
* @dev Returns the number of NFTs owned by `_owner`. NFTs assigned to the zero address are
* considered invalid, and this function throws for queries about the zero address.
* @param _owner Address for whom to query the balance.
* @return Balance of _owner.
*/
function balanceOf(
address _owner
)
external
override
view
returns (uint256)
{
require(_owner != address(0), ZERO_ADDRESS);
return _getOwnerNFTCount(_owner);
}
/**
* @dev Returns the address of the owner of the NFT. NFTs assigned to zero address are considered
* invalid, and queries about them do throw.
* @param _tokenId The identifier for an NFT.
* @return _owner Address of _tokenId owner.
*/
function ownerOf(
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
view
returns (address _owner)
{
_owner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(_owner != address(0), NOT_VALID_NFT);
}
/**
* @dev Get the approved address for a single NFT.
* @notice Throws if `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to query the approval of.
* @return Address that _tokenId is approved for.
*/
function getApproved(
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
view
validNFToken(_tokenId)
returns (address)
{
return idToApproval[_tokenId];
}
/**
* @dev Checks if `_operator` is an approved operator for `_owner`.
* @param _owner The address that owns the NFTs.
* @param _operator The address that acts on behalf of the owner.
* @return True if approved for all, false otherwise.
*/
function isApprovedForAll(
address _owner,
address _operator
)
external
override
view
returns (bool)
{
return ownerToOperators[_owner][_operator];
}
/**
* @dev Actually preforms the transfer.
* @notice Does NO checks.
* @param _to Address of a new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT that is being transferred.
*/
function _transfer(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
{
address from = idToOwner[_tokenId];
_clearApproval(_tokenId);
_removeNFToken(from, _tokenId);
_addNFToken(_to, _tokenId);
emit Transfer(from, _to, _tokenId);
}
/**
* @dev Mints a new NFT.
* @notice This is an internal function which should be called from user-implemented external
* mint function. Its purpose is to show and properly initialize data structures when using this
* implementation.
* @param _to The address that will own the minted NFT.
* @param _tokenId of the NFT to be minted by the msg.sender.
*/
function _mint(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
virtual
{
require(_to != address(0), ZERO_ADDRESS);
require(idToOwner[_tokenId] == address(0), NFT_ALREADY_EXISTS);
_addNFToken(_to, _tokenId);
emit Transfer(address(0), _to, _tokenId);
}
/**
* @dev Burns a NFT.
* @notice This is an internal function which should be called from user-implemented external burn
* function. Its purpose is to show and properly initialize data structures when using this
* implementation. Also, note that this burn implementation allows the minter to re-mint a burned
* NFT.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to be burned.
*/
function _burn(
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
virtual
validNFToken(_tokenId)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
_clearApproval(_tokenId);
_removeNFToken(tokenOwner, _tokenId);
emit Transfer(tokenOwner, address(0), _tokenId);
}
/**
* @dev Removes a NFT from owner.
* @notice Use and override this function with caution. Wrong usage can have serious consequences.
* @param _from Address from wich we want to remove the NFT.
* @param _tokenId Which NFT we want to remove.
*/
function _removeNFToken(
address _from,
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
virtual
{
require(idToOwner[_tokenId] == _from, NOT_OWNER);
ownerToNFTokenCount[_from] = ownerToNFTokenCount[_from] - 1;
delete idToOwner[_tokenId];
}
/**
* @dev Assignes a new NFT to owner.
* @notice Use and override this function with caution. Wrong usage can have serious consequences.
* @param _to Address to wich we want to add the NFT.
* @param _tokenId Which NFT we want to add.
*/
function _addNFToken(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
virtual
{
require(idToOwner[_tokenId] == address(0), NFT_ALREADY_EXISTS);
idToOwner[_tokenId] = _to;
ownerToNFTokenCount[_to] = ownerToNFTokenCount[_to].add(1);
}
/**
* @dev Helper function that gets NFT count of owner. This is needed for overriding in enumerable
* extension to remove double storage (gas optimization) of owner nft count.
* @param _owner Address for whom to query the count.
* @return Number of _owner NFTs.
*/
function _getOwnerNFTCount(
address _owner
)
internal
virtual
view
returns (uint256)
{
return ownerToNFTokenCount[_owner];
}
/**
* @dev Actually perform the safeTransferFrom.
* @param _from The current owner of the NFT.
* @param _to The new owner.
* @param _tokenId The NFT to transfer.
* @param _data Additional data with no specified format, sent in call to `_to`.
*/
function _safeTransferFrom(
address _from,
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
bytes memory _data
)
private
canTransfer(_tokenId)
validNFToken(_tokenId)
{
address tokenOwner = idToOwner[_tokenId];
require(tokenOwner == _from, NOT_OWNER);
require(_to != address(0), ZERO_ADDRESS);
_transfer(_to, _tokenId);
if (_to.isContract())
{
bytes4 retval = ERC721TokenReceiver(_to).onERC721Received(msg.sender, _from, _tokenId, _data);
require(retval == MAGIC_ON_ERC721_RECEIVED, NOT_ABLE_TO_RECEIVE_NFT);
}
}
/**
* @dev Clears the current approval of a given NFT ID.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to be transferred.
*/
function _clearApproval(
uint256 _tokenId
)
private
{
if (idToApproval[_tokenId] != address(0))
{
delete idToApproval[_tokenId];
}
}
}
/**
* @dev Optional metadata extension for ERC-721 non-fungible token standard.
* See https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-721.md.
*/
interface ERC721Metadata
{
/**
* @dev Returns a descriptive name for a collection of NFTs in this contract.
* @return _name Representing name.
*/
function name()
external
view
returns (string memory _name);
/**
* @dev Returns a abbreviated name for a collection of NFTs in this contract.
* @return _symbol Representing symbol.
*/
function symbol()
external
view
returns (string memory _symbol);
/**
* @dev Returns a distinct Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) for a given asset. It Throws if
* `_tokenId` is not a valid NFT. URIs are defined in RFC3986. The URI may point to a JSON file
* that conforms to the "ERC721 Metadata JSON Schema".
* @return URI of _tokenId.
*/
function tokenURI(uint256 _tokenId)
external
view
returns (string memory);
}
/**
* @dev Optional metadata implementation for ERC-721 non-fungible token standard.
*/
contract NFTokenMetadata is
NFToken,
ERC721Metadata
{
/**
* @dev A descriptive name for a collection of NFTs.
*/
string internal nftName;
/**
* @dev An abbreviated name for NFTokens.
*/
string internal nftSymbol;
/**
* @dev Mapping from NFT ID to metadata uri.
*/
mapping (uint256 => string) internal idToUri;
/**
* @dev Contract constructor.
* @notice When implementing this contract don't forget to set nftName and nftSymbol.
*/
constructor()
public
{
supportedInterfaces[0x5b5e139f] = true; // ERC721Metadata
}
/**
* @dev Returns a descriptive name for a collection of NFTokens.
* @return _name Representing name.
*/
function name()
external
override
view
returns (string memory _name)
{
_name = nftName;
}
/**
* @dev Returns an abbreviated name for NFTokens.
* @return _symbol Representing symbol.
*/
function symbol()
external
override
view
returns (string memory _symbol)
{
_symbol = nftSymbol;
}
/**
* @dev A distinct URI (RFC 3986) for a given NFT.
* @param _tokenId Id for which we want uri.
* @return URI of _tokenId.
*/
function tokenURI(
uint256 _tokenId
)
external
override
view
validNFToken(_tokenId)
returns (string memory)
{
return idToUri[_tokenId];
}
/**
* @dev Burns a NFT.
* @notice This is an internal function which should be called from user-implemented external
* burn function. Its purpose is to show and properly initialize data structures when using this
* implementation. Also, note that this burn implementation allows the minter to re-mint a burned
* NFT.
* @param _tokenId ID of the NFT to be burned.
*/
function _burn(
uint256 _tokenId
)
internal
override
virtual
{
super._burn(_tokenId);
if (bytes(idToUri[_tokenId]).length != 0)
{
delete idToUri[_tokenId];
}
}
/**
* @dev Set a distinct URI (RFC 3986) for a given NFT ID.
* @notice This is an internal function which should be called from user-implemented external
* function. Its purpose is to show and properly initialize data structures when using this
* implementation.
* @param _tokenId Id for which we want uri.
* @param _uri String representing RFC 3986 URI.
*/
function _setTokenUri(
uint256 _tokenId,
string memory _uri
)
internal
validNFToken(_tokenId)
{
idToUri[_tokenId] = _uri;
}
}
/**
* @dev The contract has an owner address, and provides basic authorization control whitch
* simplifies the implementation of user permissions. This contract is based on the source code at:
* https://github.com/OpenZeppelin/openzeppelin-solidity/blob/master/contracts/ownership/Ownable.sol
*/
contract Ownable
{
/**
* @dev Error constants.
*/
string public constant NOT_CURRENT_OWNER = "018001";
string public constant CANNOT_TRANSFER_TO_ZERO_ADDRESS = "018002";
/**
* @dev Current owner address.
*/
address public owner;
/**
* @dev An event which is triggered when the owner is changed.
* @param previousOwner The address of the previous owner.
* @param newOwner The address of the new owner.
*/
event OwnershipTransferred(
address indexed previousOwner,
address indexed newOwner
);
/**
* @dev The constructor sets the original `owner` of the contract to the sender account.
*/
constructor()
public
{
owner = msg.sender;
}
/**
* @dev Throws if called by any account other than the owner.
*/
modifier onlyOwner()
{
require(msg.sender == owner, NOT_CURRENT_OWNER);
_;
}
/**
* @dev Allows the current owner to transfer control of the contract to a newOwner.
* @param _newOwner The address to transfer ownership to.
*/
function transferOwnership(
address _newOwner
)
public
onlyOwner
{
require(_newOwner != address(0), CANNOT_TRANSFER_TO_ZERO_ADDRESS);
emit OwnershipTransferred(owner, _newOwner);
owner = _newOwner;
}
}
/**
* @dev This is an example contract implementation of NFToken with metadata extension.
*/
contract MyArtSale is
NFTokenMetadata,
Ownable
{
/**
* @dev Contract constructor. Sets metadata extension `name` and `symbol`.
*/
constructor()
public
{
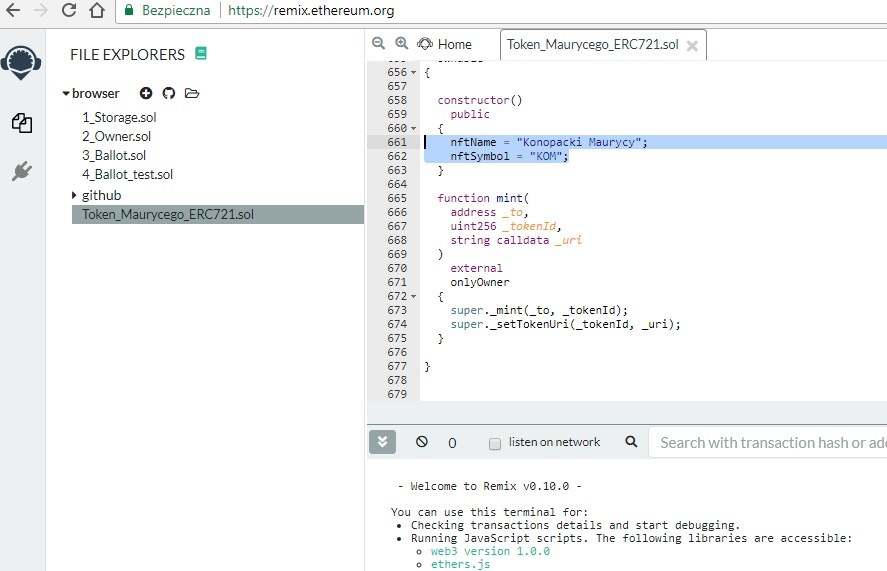
nftName = "Konopacki Maurycy";
nftSymbol = "KOM";
}
/**
* @dev Mints a new NFT.
* @param _to The address that will own the minted NFT.
* @param _tokenId of the NFT to be minted by the msg.sender.
* @param _uri String representing RFC 3986 URI.
*/
function mint(
address _to,
uint256 _tokenId,
string calldata _uri
)
external
onlyOwner
{
super._mint(_to, _tokenId);
super._setTokenUri(_tokenId, _uri);
}
}
5) Wyszukujemy (najlepie użyć skrótu klawiszowego CTRL+F) i wpisujemy nasze parametry:
nftName = "Konopacki Maurycy"; <- nazwę naszego tokenu np. CrytpoCities nftSymbol = "KOM"; <- skrót/symbol tokenu np. CK
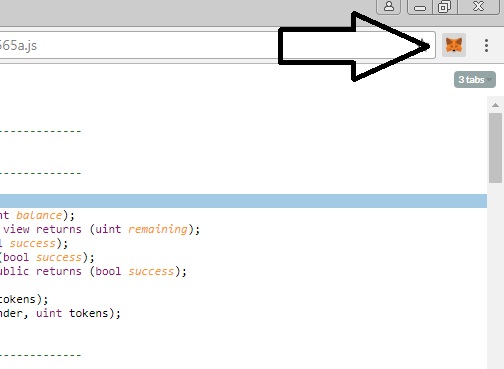
6) Kolejnym krokiem jest zainstalowanie portfela MetaMask w formie wtyczki (plugina) na naszą przeglądarkę. MetaMask to portfel obsługujący Ethereum i tokeny, które się na nim znajdują:
Po zainstalowaniu – portfel powinien się pojawić w prawym górnym rogu naszej przeglądarki:
7) Po założeniu portfela wchodzimy na nasz w MetaMask i zmieniamy na sieć testową “Ropsten”. Token możemy tworzyć na głównym łańcuchu Ethereum oraz na testowych, dla treningu warto potrenować na testowych sieciach.
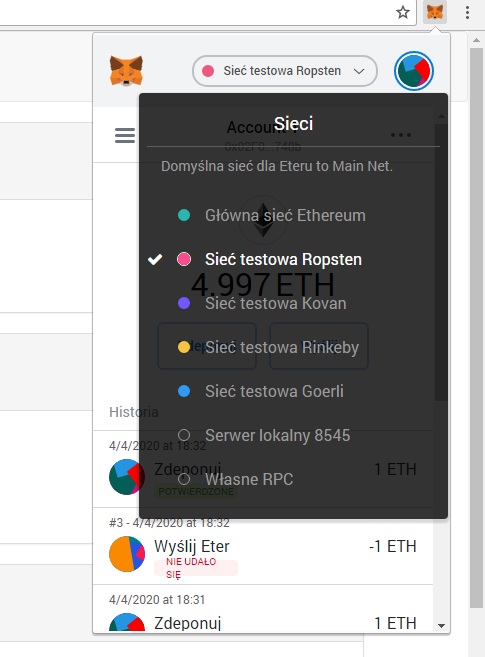
Następnie kopiujemy nasz adres portfela:
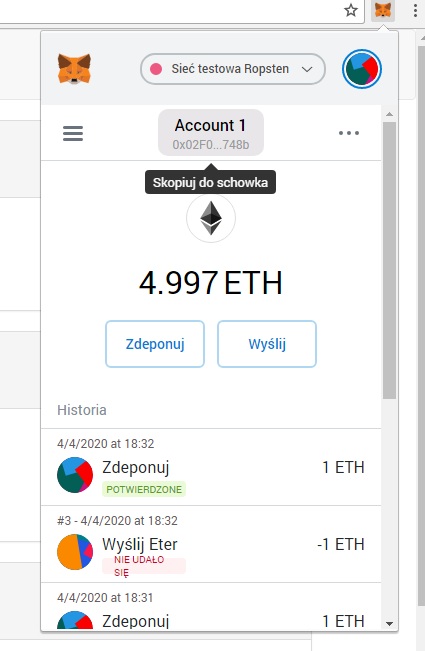
8) Po przekopiowaniu naszego adresu wchodzimy na kranik (faucet) – dzięki któremu uzyskamy trochę testowych ETH:
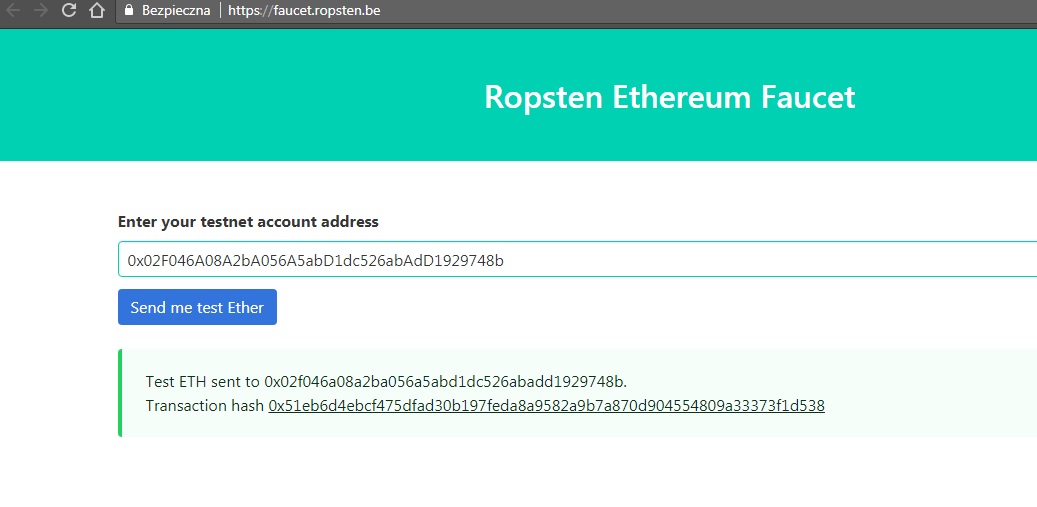
Po kliknięciu “Send me test Ether” pojawi się potwierdzenie wysłanych testowych ETH, które wygląda identycznie jak na głównym łańcuchu ETH:
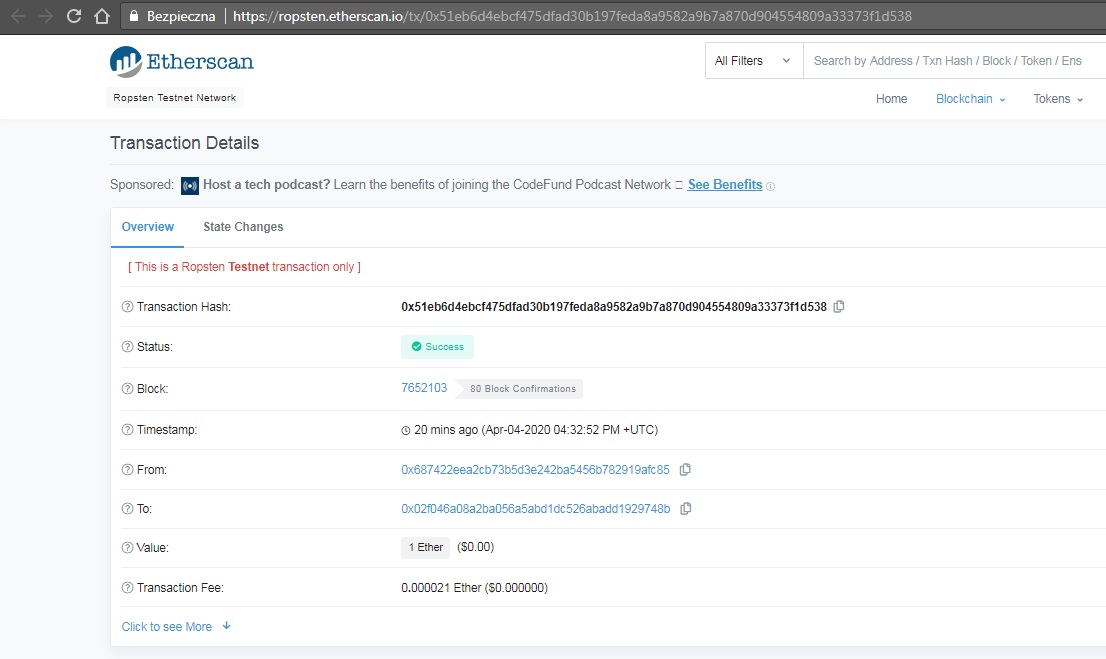
Do “wpuszczenia” w sieć naszego tokenu potrzebujemy jedynie dwóch wtyczek na platformie Remix. Wracamy na stronę https://remix.ethereum.org/ i wchodzimy w “PLUGIN MANAGER”:
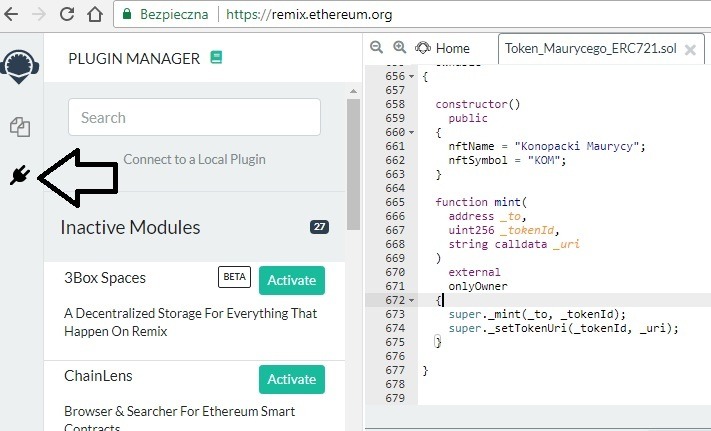
W “search” wpisujemy:
- Solidity compiler;
- Deploy & run transactions;
– aktywujemy obie wtyczki.
9) Wchodzimy w “Solidity compiler” i z listy wyszukujemy wersję 0.6.2+commit.bacdbe57:
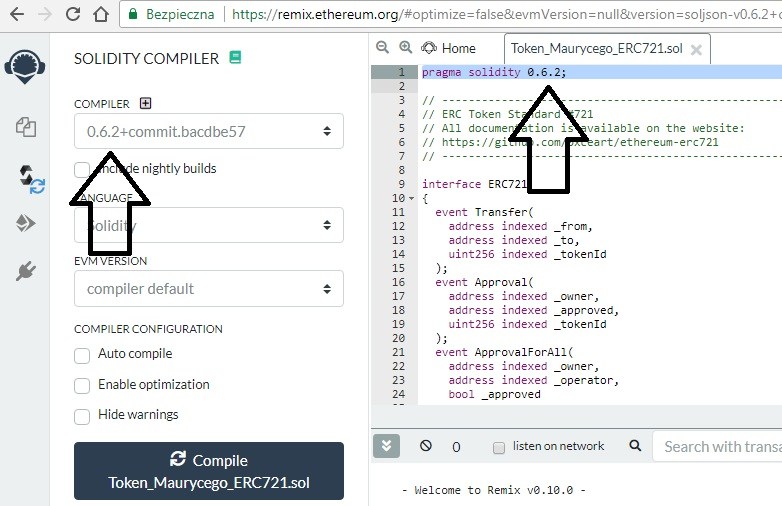
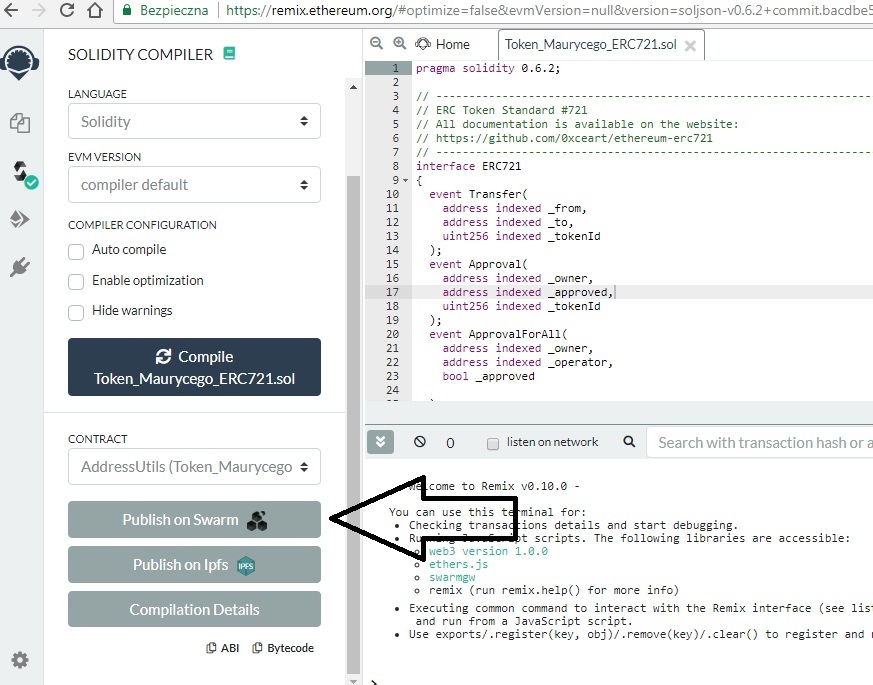
Klikamy “Compile Token_Maurycego.sol” – oczywiście tutaj będzie nazwa Waszego projektu. Plugin sprawdza poprawność naszego smart contractu – może to potrwać do minuty przy weryfikacji kodu tokenu. Jeśli nasz kod będzie poprawny – wyświetli nam się informacja o możliwości publikacji i sprawdzeniu szczegółów – “Publish on Swarm“, “Publish on Ipfs” i “Compilation Details“:
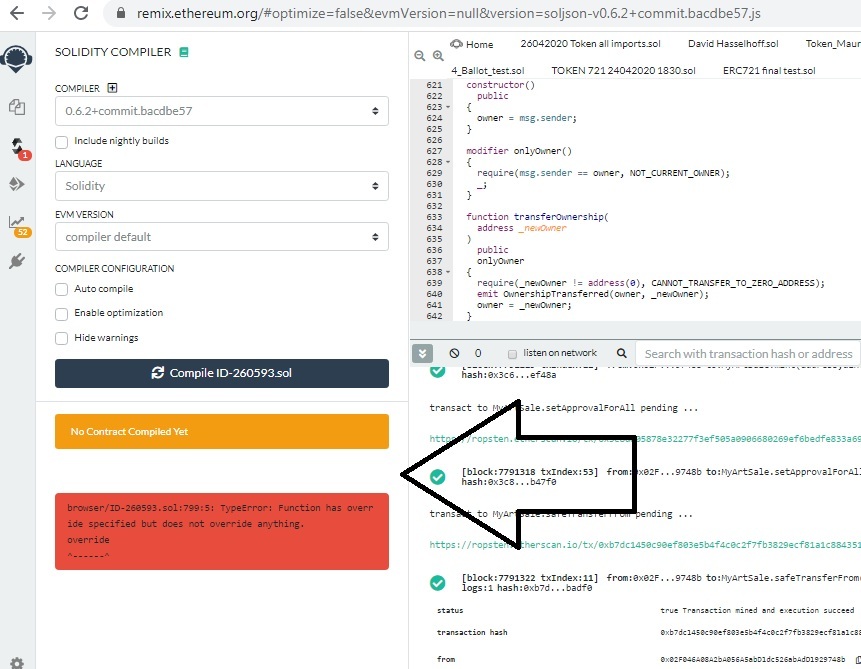
Jeśli mamy błąd to wyświetli się następujący komunikat informujący, gdzie jest “niespójność”:
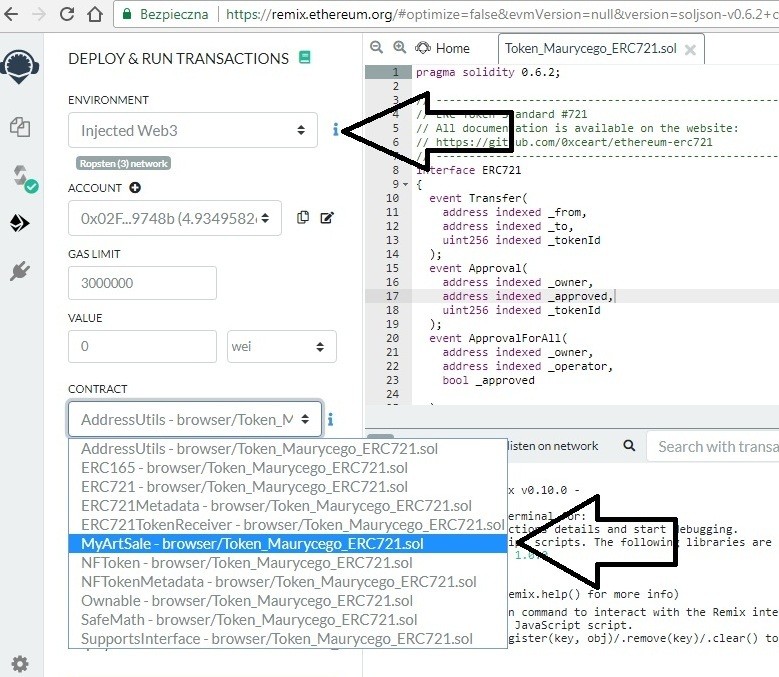
10) Wchodzimy w “Deploy & run transactions”. Z “Environment” wybieramy “Injected Web3” oraz z “CONTRACT” MyArtSale – browser/’Tutaj będzie nazwa naszego projektu’.sol. Jeśli instalowaliśmy portfel MetaMask w trakcie pracy na remix.ethereum.org, wówczas konieczne będzie odświeżenie strony i ponowne skompilowanie naszego kodu.
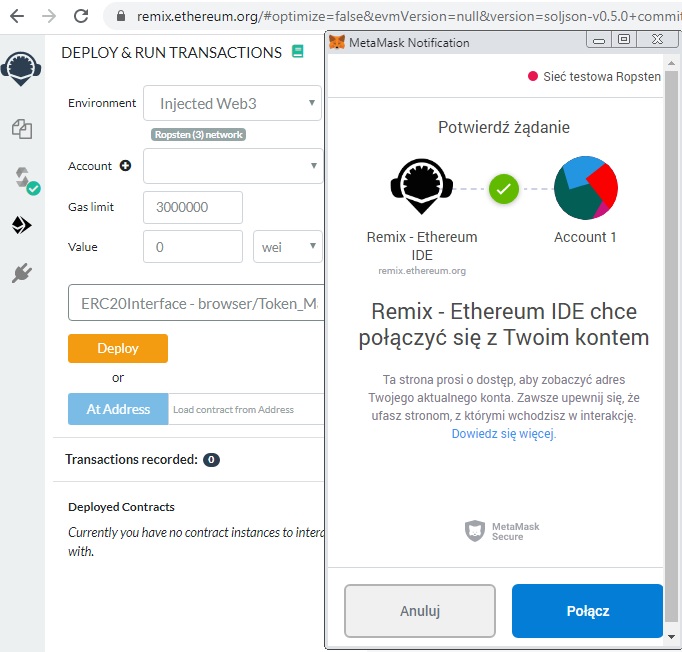
Wirtualna maszyna ETH będzie prosiła o połączenie z naszym portfelem MetaMask:
*Oczywiście jeśli zmienimy sieć na główny łańcuch to smart contract będzie tam funkcjonował:
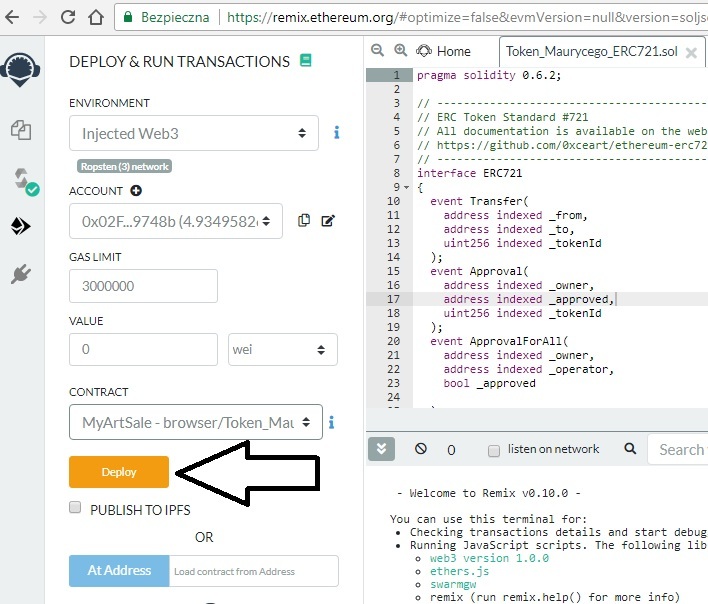
Klikamy “Deploy”, aby nasz smart contract w formie tokenu został stworzony:
IDE poprosi nas o uiszczenie opłaty za stworzenie smart contractu w formie GAS-u (mały ułamek ETH):
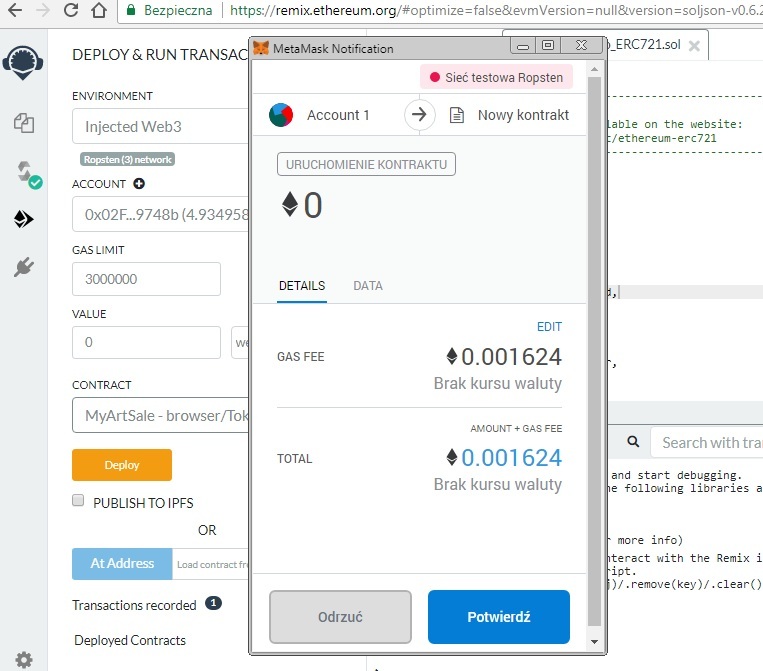
Klikamy “Potwierdź” i czekamy kilkanaście sekund na stworzenie naszego smart contractu:
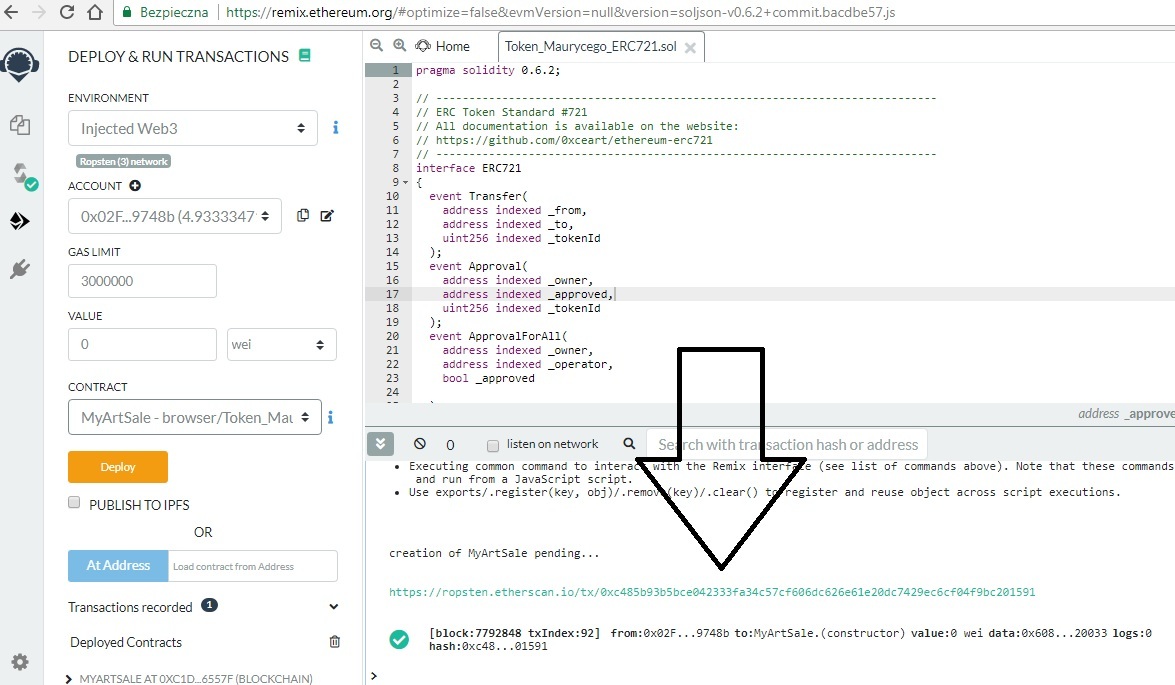
Na explorerze wygląda to następująco:
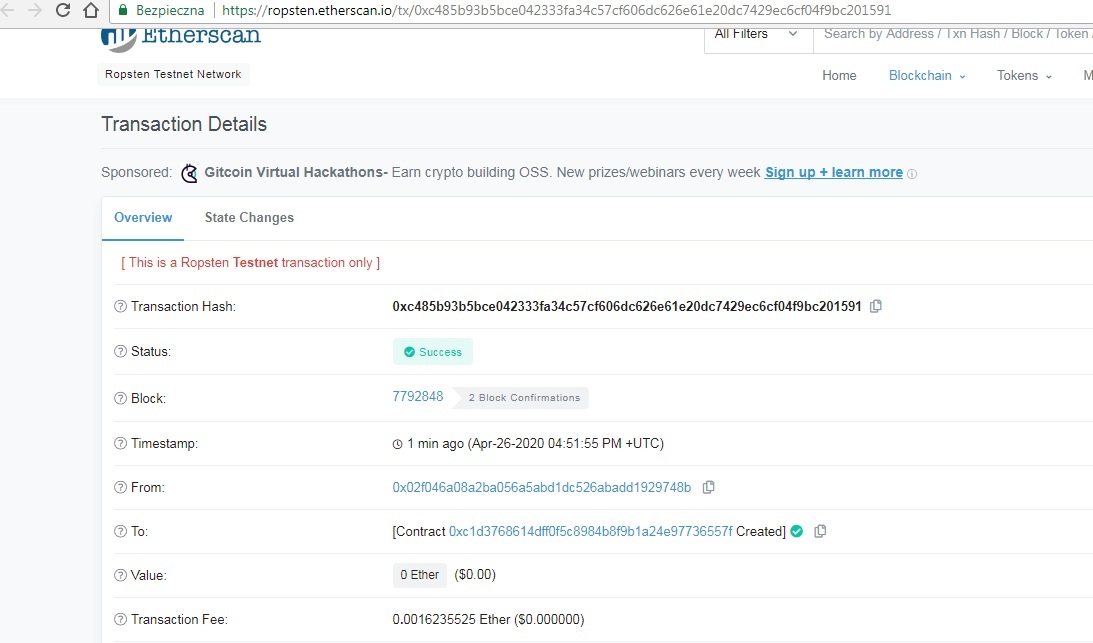
11) Wysyłanie tokenu ERC-721 na konkretny adres z danym ID.
Rozwijamy “MYARTSALE ATOXC1D…6557F (BLOCKCHAIN)”.
W miejscu “mint”:
_to: address <- obowiązkowo wypełniamy - wpisujemy adres na który ma trafić token ERC-721
_tokenId: unit256 <- opcjonalnie wypełniamy - ID, czyli jego unikalność (będzie tylko jeden
z takim ID w ramach naszego tokenu) np. 1 lub 432523. Jeśli pozostawimy
puste pole ID będzie "0"
_url: string <- opcjonalnie wypełniamy - tekst, który będzie możliwy do rozkodowania
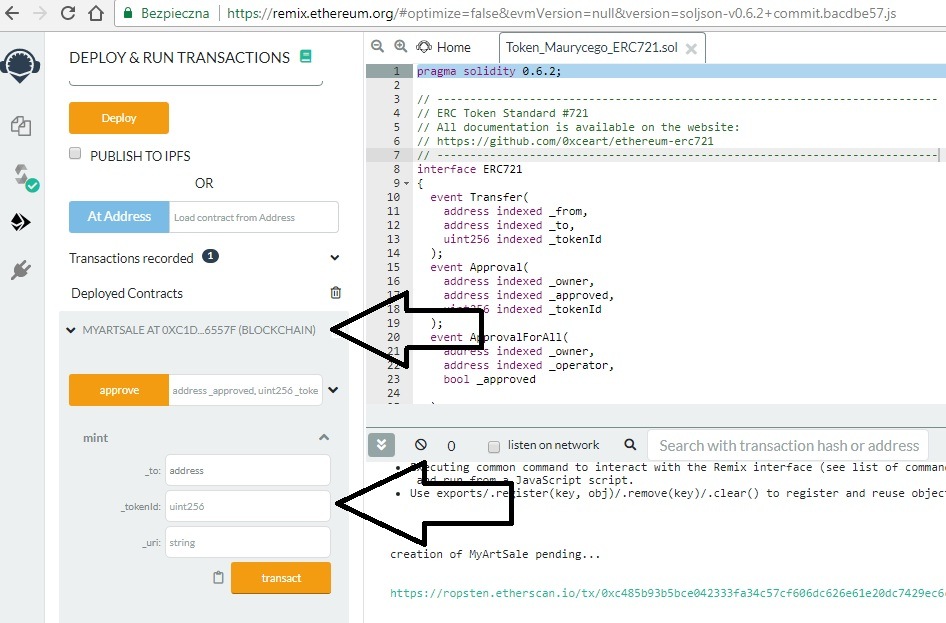
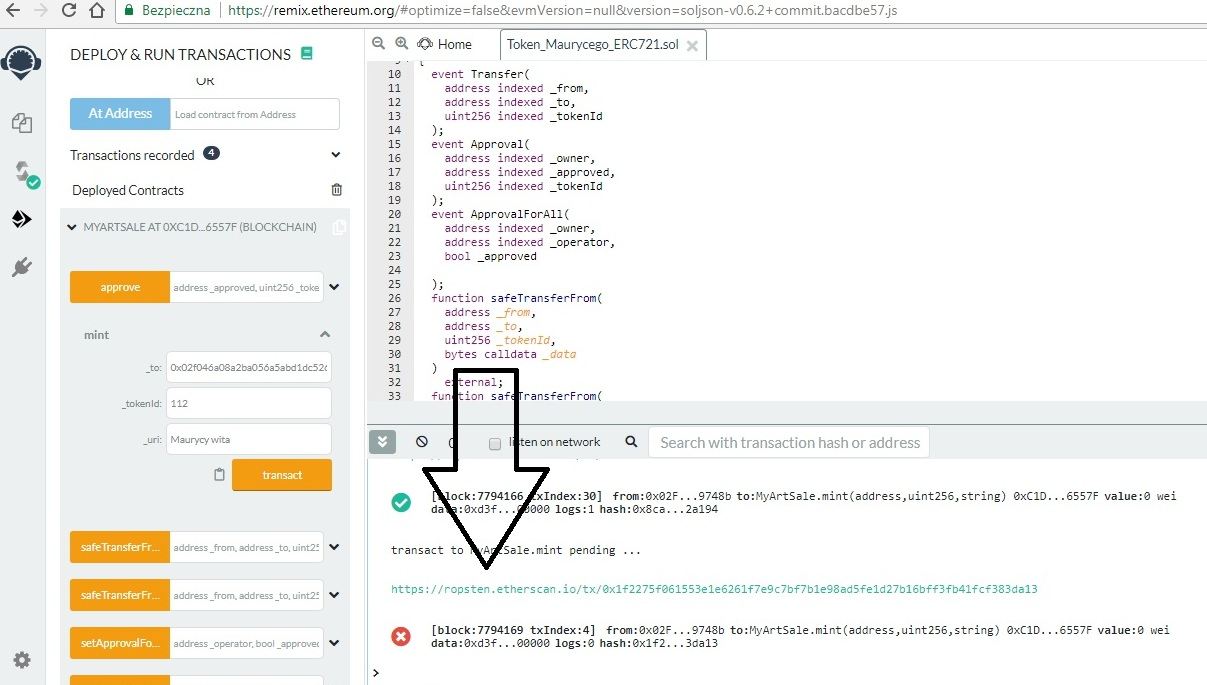
Po kliknieciu “transact” poprosi nas, aby uiścić opłatę za dokonanie “transakcji” na smart contracie (procedura identyczna jak podczas generowania smart contractu). Po opłaceniu pojawi się “hash” którym będziemy mogli podejrzeć przebieg “transakcji”:
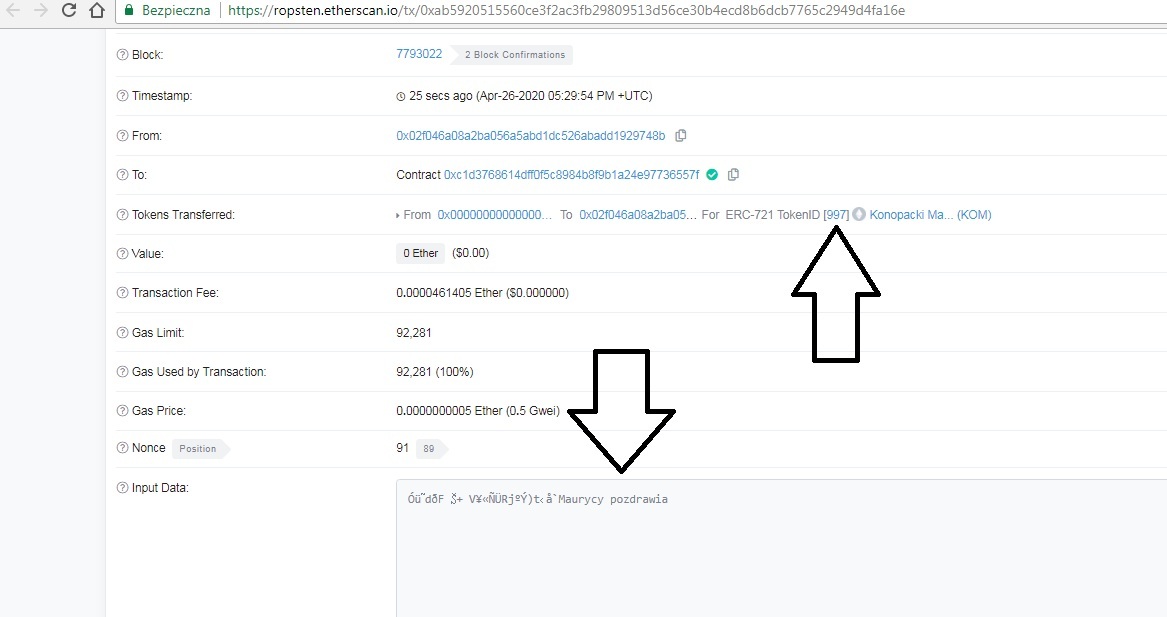
Wchodząc na nasz adres na explorerze zauważymy, że pojawi się kolumna “Erc721 Token Txns” – będą tam zawarte wszystkie transakcje, które są związane z tokenami ERC-721:
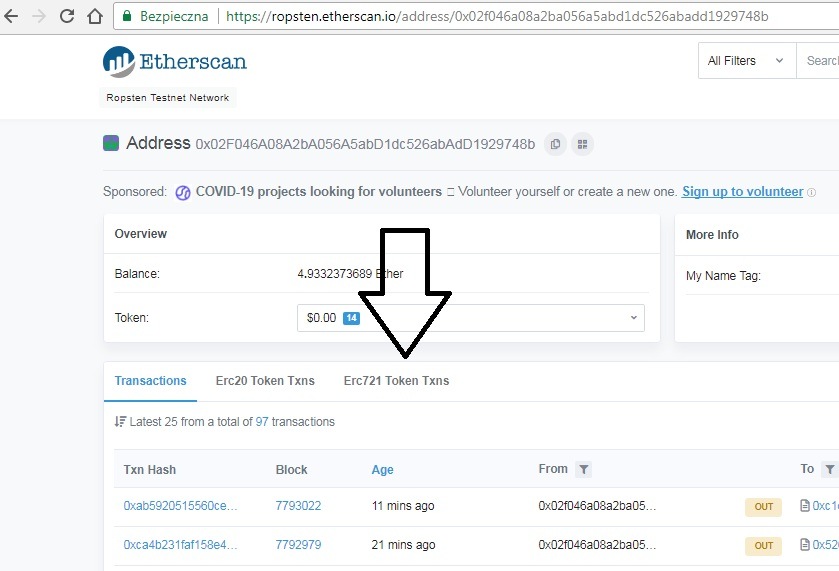
Próba wysłania drugiego takiego tokenu z istniejącym już ID pod naszym smart contractem spotka się z odmową, gdyż może istnieć tylko jedno ID przypisane dla jednego smart contractu. Takich ID możemy wyemitować nieskończenie wiele:
Token możecie dodać również w MetaMasku (lub innym portfelu). Informacje o tym jak to zrobić znajdziecie w artykule Jak stworzyć własny token ERC-20? [Ethereum] w punkcie 12.
Podsumowanie
Tokeny w formacie ERC-721 są znacznie mniej popularne od ERC-20, lecz pojawia się ich coraz więcej, gdyż ich potencjał jest ogromny. Smart contract nie jest trudny do napisania. Najczęściej tworzone są w celu potwierdzenia istnienia danego produktu jak np. karty kolekcjonerskiej lub oryginalnego obuwia. W przyszłości mogą służyć w takich dziedzinach jak nieruchomości (ewidencja gruntów) czy prawo (notariat).
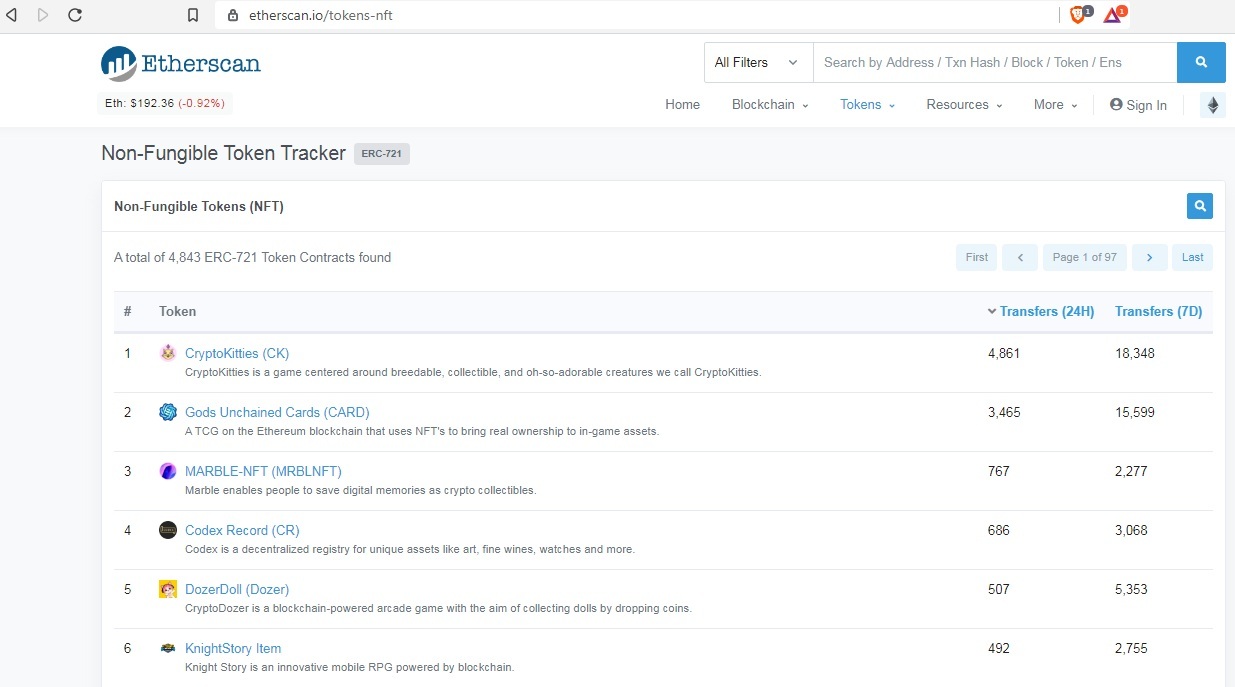
Na stronie https://etherscan.io/tokens-nft możemy sprawdzić aktualne statystyki związane z ilością tokenów ERC-721 (wyszczególnione są tokeny, które posiadają największy ruch):
Śledź CrypS. w Google News. Czytaj najważniejsze wiadomości bezpośrednio w Google! Obserwuj ->
Zajrzyj na nasz telegram i dołącz do Crypto. Society. Dołącz ->


































Aktualnie brak komentarzy.